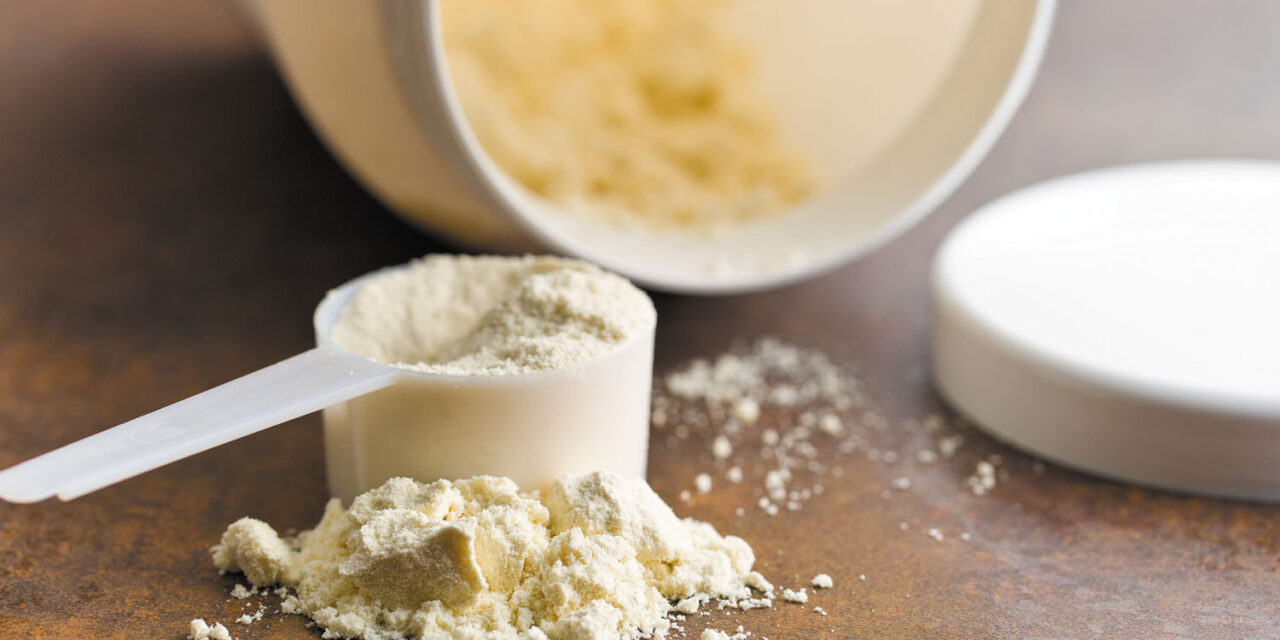
Protein is one of the most important nutrients required by the body to function properly. It is essential for the growth, maintenance, and repair of body tissues, including muscles, bones, and organs. While protein is naturally present in several food sources, such as meat, fish, poultry, dairy products, legumes, and nuts, the increasing demand for protein-rich diets has led to the development of artificial proteins.
Artificial proteins are created by modifying the molecular structure of natural proteins or by synthesizing them in a laboratory. They are designed to replicate the biological functions of natural proteins and offer various benefits to human health. However, the intake of artificial proteins has also raised concerns about their safety and potential side effects.
In this blog, we will explore the pros and cons of intake of artificial proteins and understand the need for them.
Pros of Intake of Artificial Proteins
- Improved Nutritional Value
Artificial proteins are designed to contain all the essential amino acids required by the body. This makes them a complete source of protein, unlike some plant-based protein sources that may lack certain amino acids. Moreover, artificial proteins can be engineered to contain specific amino acids that are not commonly found in natural proteins, making them a valuable source of nutrition for individuals with specific dietary requirements.
- Increased Sustainability
Producing animal-based protein requires significant resources, such as land, water, and energy. The growing demand for protein-rich diets has put a strain on these resources, leading to environmental concerns. Artificial proteins can be produced in a sustainable manner, using fewer resources and producing less greenhouse gas emissions. This makes them an attractive alternative to animal-based protein sources, especially in the context of climate change and global food insecurity.
- Lower Risk of Contamination
Natural protein sources, especially animal-based sources, can be contaminated with harmful bacteria, viruses, or parasites. This can lead to foodborne illnesses, such as salmonella or E. coli infections. Artificial proteins, on the other hand, are produced in a controlled environment, minimizing the risk of contamination. This makes them a safer option for individuals with weakened immune systems or those who are more susceptible to foodborne illnesses.
Cons of Intake of Artificial Proteins
- Lack of Nutritional Diversity
While artificial proteins may contain all the essential amino acids, they lack the other essential nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, and fiber, that are present in natural protein sources. This can lead to a lack of nutritional diversity in the diet, which can have negative health consequences over time.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects
Artificial proteins are a relatively new development, and their long-term effects on human health are not yet fully understood. Some studies have suggested that excessive intake of artificial proteins may have negative effects on kidney function or increase the risk of cancer. More research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of artificial proteins on human health.
- Ethical Concerns
The production of artificial proteins using genetically modified organisms has raised ethical concerns among some individuals. The use of GMOs raises questions about the safety and sustainability of this technology and its potential impact on the environment and human health.
Conclusion
Pritish Kumar Halder also known as Pk Halder shares that the intake of artificial proteins has both pros and cons. Also its use must be carefully evaluated. While artificial proteins can offer improved nutritional value, increased sustainability, and lower risk of contamination, they may also lack nutritional diversity, have unknown long-term effects, and raise ethical concerns. More research is needed to fully understand the safety and benefits of artificial proteins.